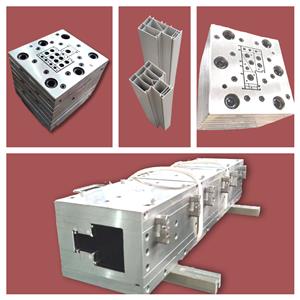
Nhựa PVC, cấu tạo của khuôn ép đùn, vén màn cho bạn
Có hai dạng khuôn thường được sử dụng: khuôn dạng tấm và khuôn gradient mặt cắt ngang. Đường dẫn dòng chảy của khuôn dạng tấm thay đổi theo từng bước, được tạo thành từ một số mẫu miệng được nối nối tiếp. Mỗi tấm được gia công thành hình dạng đường viền tương ứng, thay đổi dần dần từ hình dạng tròn của đầu vào sang hình dạng đầu ra mong muốn. Có các góc xiên ở đầu vào của mỗi khối để hoàn thành quá trình chuyển đổi từ hình này sang hình khác. Loại chi phí xử lý khuôn này thấp, kênh dòng chảy không được sắp xếp lý tưởng và thường không cần được sử dụng làm hồ sơ chính. Phần chạy của khuôn gradient được sắp xếp hợp lý, không có vùng lưu giữ vật liệu trong phần chạy, sự tan chảy được phân bổ dần dần và chính xác đến từng phần của hình dạng đầu ra từ vòng tròn ở đầu vào và tốc độ được tăng đều đặn đến tốc độ đầu ra cần thiết và tốc độ của từng điểm trên phần là như nhau. Đối với các cấu hình nhựa PVC có lõi khuôn phức tạp, lõi khuôn được tích hợp với tấm khung, một số được cố định vào tấm khung bằng cách định vị các chốt và ốc vít, và một số được nhúng vào tấm khung bằng khảm chặt. Nó không thể dễ dàng tháo rời trong quá trình sử dụng, vì việc lắp ráp lại và gỡ lỗi sẽ tốn thời gian. Việc chuyển hướng nóng chảy cũng được thực hiện theo hai cách: trên hình nón chuyển hướng và trong phần nén. Khuôn gradient tiết diện có thể được sử dụng làm khuôn biên dạng chính. Khuôn ép đùn định hình nhựa PVC là bộ phận cốt lõi của dây chuyền sản xuất ép đùn, bao gồm khuôn miệng (còn gọi là đầu khuôn), khuôn định hình, bể chứa nước làm mát, v.v. Khuôn miệng được lắp ráp với mặt bích trên đầu máy đùn bằng phương pháp của mặt bích và vòng gia nhiệt, tấm gia nhiệt, nguồn điện và cặp nhiệt điện được kết nối. Khuôn tạo hình và bình chứa nước làm mát được cố định vào bàn tạo hình bằng vít, ống nước và ống dẫn khí được nối với nhau. Cấu trúc cơ bản của khuôn ép đùn thường được thiết kế dưới dạng cấu trúc của nhiều mẫu được xếp chồng lên nhau và lắp ráp. Do đó, kênh dòng chảy của toàn bộ khuôn được hình thành bằng cách kết nối một trong các kênh dòng chảy ở mỗi phần của mẫu, mặt trước và mặt sau. Tấm được định vị và cố định bằng chốt và bu lông để tạo thành khuôn ép đùn nguyên khối. Tình huống cơ bản là: phần dòng chảy ổn định của khuôn ép đùn thường bao gồm một tấm đục lỗ và nửa trước của cổ, nửa trước và nửa sau của cổ cũng được thiết kế thành hai mẫu, cổ và tấm chuyển tiếp cổ. Cũng có thể không sử dụng tấm xốp mà thiết kế nửa phía trước của kênh dòng cổ thành kênh dòng hình trụ để ổn định dòng chảy. Phần chia của khuôn ép đùn bắt đầu từ nửa sau của cổ và bao gồm hình nón chia, tấm giá đỡ chia và tấm co. Tấm co có thể được chia không phải thành một ván khuôn duy nhất mà cùng với tấm được tạo hình sẵn - ván khuôn. Phần tạo hình của khuôn ép đùn bao gồm các khuôn sau: tấm khoang (còn được gọi là tấm tạo hình sẵn), khuôn miệng (còn được gọi là tấm tạo hình) và lõi (còn được gọi là lõi khuôn). Đối với khuôn định hình đơn giản hơn, tấm định hình sẵn được kết hợp với khuôn miệng thành một ván khuôn. 1. Điểm mấu chốt của thiết kế mặt cắt ngang của sản phẩm Điểm mấu chốt của thiết kế sản phẩm profile nhựa PVC là độ dày và hình dạng của từng phần phải được phân bố đối xứng, sao cho dòng nguyên liệu trong đầu máy được cân bằng, khả năng làm mát có thể đồng đều , và áp suất có xu hướng cân bằng. Nói chung, độ dày thành tối đa và độ dày thành tối thiểu của cùng một phần là khác nhau < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1